
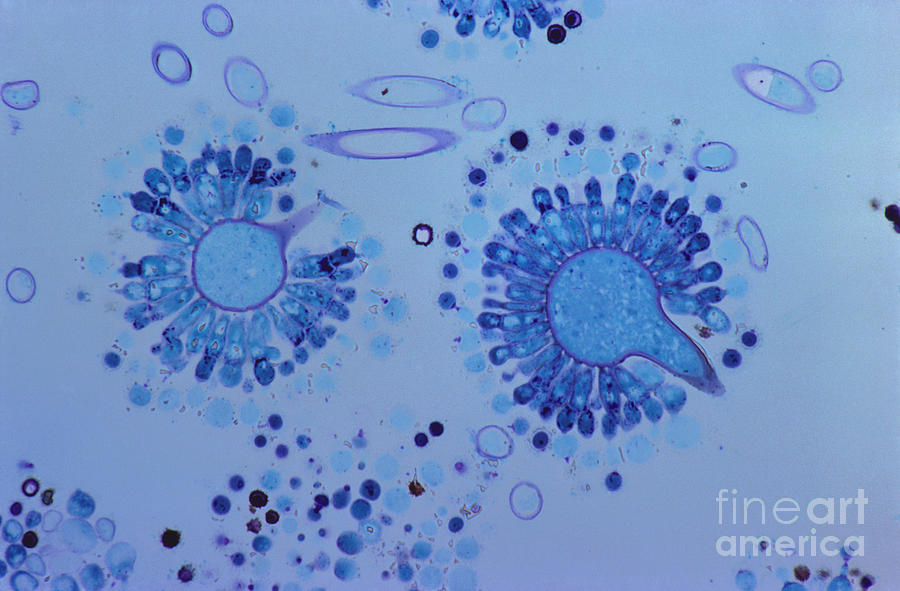
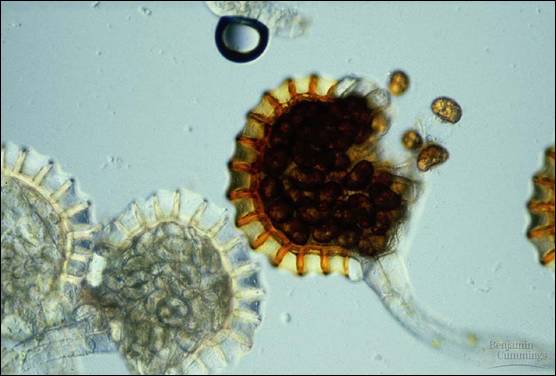
Studying about the characteristics of fungi is quite fascinating. Read on to know more about the procreation process of fungi in this BiologyWise article. Cyst has nothing to do with the reproduction of the cell. Production of spores is observed in both these types of reproduction, though the genetic makeup of the spores varies. A spore is the reproductive part having a protective covering as a spore for its germination has to face harsh environmental conditions such as air currents whereas cyst is the group of cells which come together to protect themselves from harsh conditions. The zygospore will remain dormant until conditions become favorable once again. Reproduction in fungi takes place by asexual or sexual means. Leukemia SPORE Advisory Committee (2003-present). These sex cells fuse to become a diploid zygospore. The spores are diploid cells containing genetic information about the plant itself, thus making it capable of asexual reproduction. NCI Specialized Program of Research Excellence (SPORE) Grant in Breast. During times when conditions are unfavorable for development, the algae undergo sexual reproduction to produce gametes. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. The spores are haploid and are produced by mitosis. We hypothesize that these relationships are owing to water balance optimization, driven by water storage in spores as a critical factor for successful germination of primary mycelia in the drier micro-environments found earlier in the fruiting season and/or in continental climates.The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. In separate analyses, significant relationships were observed between spore size and climate factors. Unlike gametes in sexual reproduction, spores do not need to fuse in order for reproduction to take place. They are typically single-celled and have the ability to develop into a new organism. Small-spored species dominate in the oceanic parts of Norway, whereas large-spored species are typical of more continental parts. Spores are reproductive cells in plants algae and other protists and fungi. We found a strong relationship between spore size and time of fruiting on average, a doubling of spore size (volume) corresponded to 3 days earlier fruiting. This study of relationships between morphological and ecological characteristics, climate factors and time of fruiting are based upon thorough statistical analyses of 66 520 mapped records from Norway, representing 271 species of autumnal fruiting mushroom species. Although spores are known from older rocks, cryptospore and trilete spores are thought. However, little is known about the selective forces that have resulted in some species fruiting early and others later in the fruiting season. The main difference between spores and seeds is that spores do not contain stored food resources and require more favorable conditions for the germination whereas seeds contain stored food in their endosperm, enabling them to germinate in harsh conditions as well. Trilete spores, which divide via meiosis to form a tetrad of cells that disperse separately, first appeared in the late Late Ordovician and form a rare, geographically isolated component in cryptospore assemblages. 1 A chief difference between spores and seeds as dispersal units is that spores have very little. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and some protozoans. Sexual spores are fewer in number than asexual spores. In biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersion and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions.
Due to its strict anaerobic requirements, the infectious and transmissible morphotype is the dormant spore.

Most basidiomycete fungi produce annual short-lived sexual fruit bodies from which billions of microscopic spores are spread into the air during a short time period. As a result of sexual reproduction sexual sores are produced. Clostridium difficile is a Gram-positive, spore-forming obligate anaerobe and a major nosocomial pathogen of world-wide concern.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
